Wire Grid Polarizer – 10% Improvement in PBS Efficiency
Application Notebook
This technical brief compares imaging needs and how Moxtek is improving its products. It explains how competing technologies in LCoS projectors compare in terms of brightness, performance, durability and reliability.
The ProFlux® Nanowire® polarizer technology offers a reliable, highly durable solution to high quality LCoS display technology with a perfect polarization match to the LC imager. Recent improvements in the polarizing beam splitter (PBS) technology enable a 10% improvement in efficiency.
This technical brief compares imaging needs and how Moxtek is improving its products. It explains how competing technologies in LCoS projectors compare in terms of brightness, performance, durability and reliability.
PBS Efficiency
Efficiency (Tp*Rs) for a polarizing beamsplitter is a measure of how perfectly a polarizer converts randomly polarized light into (reflected) s and (transmitted) p polarized light. If all of the light is converted, then the beamsplitter would be 100% efficient. In reality, some of the light is absorbed, some 's' is transmitted and some 'p' is reflected, reducing the efficiency.
The Moxtek standard PBS is typically 81% efficient at 550 nm wavelength. Recently, with improved manufacturing techniques and new wire grid technology, this efficiency has been dramatically improved.
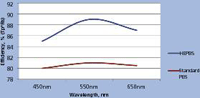
Figure 1: Beamsplitter efficiency comparison (typical).
Figure 1 shows the improvement in efficiency for the Moxtek High Efficiency PBS (HEPBS) versus standard PBS. This represents a 10% improvement and is greater than 89% efficiency at 550 nm wavelength.
Comparison of Other Technologies
In addition to high efficiency, ProFlux Nanowire® grids offer many other benefits. Table I, "Comparison of Technologies," shows a comparison of Nanowire® grid polarizers, stretched polymer absorbing films (dichroic polarizers), and Brewster's angle polarizers (MacNeille cubes).
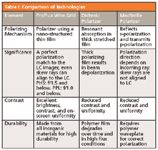
Table I: Comparison of technologies
Flatter response of ProFlux across both wavelength and angle creates a more uniform picture from the projector. The wide acceptance angle allows for small f/# optical designs while maintaining color and contrast uniformity. ProFlux offers an excellent, flat response to rotation in both axes, an indication of its superior performance with skew ray polarization. Contrastingly, dichroic sheet depolarization reduces the ability to maintain high polarization contrast in optical systems.
The Profulx beam splitter shows no total internal reflection cutoff, and may be used at a much smaller f/# than the MacNielle PBS, retaining high contrast.
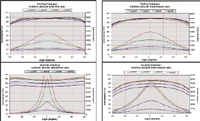
Figure 2: AOI comparison for ProFlux wire grid and dichroic polarizers.
An important advantage of the ProFlux PBS over a MacNeille cube is the direction of polarization. A cube polarizes in a direction defined by the orientation of the incoming ray, that is, by the plane of incidence. Because the plane of incidence changes as the skew ray direction changes, uniform polarization over a large cone is impossible for a standalone cube PBS.
ProFlux PBS, on the other hand, polarizes relative to the direction of the wire grid structure. Rays along the principal axis, as well as skew rays, are all polarized in the same direction. This has been called a Cartesian polarizer and is a critical quality for good PBS polarization. Using ProFlux PBS polarizers creates improved full screen performance by providing uniform polarization brightness and contrast across the entire angular aperture at the PBS.
Moxtek
452 West 1260 North, Orem, UT 84057
tel. (800) 758-3110
Email: info@moxtek.com; Website: www.moxtek.com

Thermo Fisher Scientists Highlight the Latest Advances in Process Monitoring with Raman Spectroscopy
April 1st 2025In this exclusive Spectroscopy interview, John Richmond and Tom Dearing of Thermo Fisher Scientific discuss the company’s Raman technology and the latest trends for process monitoring across various applications.
A Seamless Trace Elemental Analysis Prescription for Quality Pharmaceuticals
March 31st 2025Quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure compliance with standards like United States Pharmacopoeia <232> and ICH Q3D, as well as FDA regulations. Reliable and user-friendly testing solutions help QA/QC labs deliver precise trace elemental analyses while meeting throughput demands and data security requirements.