ICP-MS Studies of Plutonium in the Environment
Special Issues
Plutonium is distributed globally in the Earth's surface environment as a result of atmospheric weapons tests, nuclear accidents, and nuclear fuel reprocessing. Mass spectrometry (MS), in particular, sector field ICP-MS, now is used widely to determine Pu activities and isotope ratios; 240Pu/239 is very useful in determining Pu origin. Determination of Pu by ICP-MS involves dissolution, column separation, and the MS determination; detection limits are 0.1–10 fg for each isotope. Applications of the determination of sector field ICP-MS to studies of environmental Pu include discerning sources of contamination near the Chernobyl reactor, and chronology of recent aquatic sediments.
Origins of Environmental Plutonium
Produced through successive neutron capture processes in a reactor or bomb that initially begin with 235U or 238U, plutonium (Pu) has become widely distributed in the Earth's surface environment as a result of human activities during the last six decades. With minor exceptions, Pu in the environment is entirely of anthropogenic origin. Plutonium in the Earth's surface environment consists principally of five isotopes: 238Pu (t1/2 = 87.74 y), 239Pu (t1/2 = 24110 y), 240Pu (t1/2 = 6563 y), 241Pu (t1/2 = 14.4 y), and 242Pu (t1/2 = 373,000 y). The isotopes 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, and 242Pu all decay by emission of α particles, while 241Pu undergoes β decay to produce 241Am. The uppermost 30 cm of undisturbed Earth's crust has 239Pu concentrations ~104 –105 times greater than natural (neutron capture–produced) concentrations. No evidence to date has identified nonanthropogenic sources for the isotopes 240Pu, 241Pu, and 242Pu. Approximately 6000 kg of 239Pu, along with smaller masses of 240Pu, 241Pu, and 242Pu, has been deposited onto the Earth's surface, mainly as a result of atmospheric weapons tests conducted in the 1950s and 1960s.
The U.S. conducted low-yield above-ground tests at the Nevada Test Site (NTS) from 1951 to 1962, and high-yield tests were conducted between 1952 and 1962 at the Pacific Proving Grounds. Atmospheric deposition of Pu and associated fission products such as 90Sr was pronounced in the 1950s and 1960s, with a pronounced and well known maximum in the 1963–1964 timeframe, followed by a sharp decrease in deposition. The decrease in deposition coincided with the 1963 Limited Test Ban Treaty, signed by the U.S., former Soviet Union, and U.K. Figure 1 illustrates the annual deposition of 90Sr in New York, NY during the time interval 1954–1980 (1). Samples were collected monthly between 1954 and 1976, and quarterly thereafter. Evident in this curve is the small peak in 1959, a "moratorium" in 1960–1961 corresponding to the suspension of U.S. and Soviet testing, and the maximum deposition in 1963. The curve for 90Sr is a very close approximation of the Pu deposition curve, as both of these species were deposited primarily through the same stratospheric delivery mechanism. A similar deposition chronology is observed at locations worldwide.

Figure 1. Deposition of the fission product, 90Sr, at a U.S. Government monitoring location in New York, NY, during the timeframe 1954â1980.
While the localized deposition of Pu and fission products was relatively uniform, deposition was highest in the mid-latitude regions of the northern hemisphere, and in regions of highest precipitation, as rain and snow removed fallout radionuclides from the troposphere after their re-entry from the stratosphere. At 40° N, the inventory (cumulative, depth-integrated deposition per unit area) of 239+240Pu is ~50–100 Bq/m2 and the surface Pu activities are ~2 Bq/kg. This activity corresponds to mass concentrations of ~500 and 90 fg/g for 239Pu and 240Pu, respectively.
Plutonium isotopic compositions vary according to the mode of production of this element. As examples, "weapons-grade" Pu consists mainly of 239Pu, and 240Pu/239Pu atom ratios of ~0.03–0.07 are typical. Pu from low-yield fission tests, such as at the NTS, exhibits 240Pu/239Pu unaltered from the Pu contained in the original device. The isotopic composition of stratospheric fallout Pu has been compiled by Kelley et al. (2), who used thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) for measurements of 54 worldwide samples. At 31–70° N, average atom ratios (± 2 σ) are: 240Pu/239Pu, 0.180 ± 0.014; 241 Pu/239 Pu, 0.00194 ± 0.00028; and 242Pu/239Pu, 0.00387 ± 0.00071. However, Pu that has been subjected to lengthy neutron activation in power reactors contains relatively larger abundances of the heavier isotopes (3). The Pu isotopic composition, therefore, can provide a "fingerprint" of different sources and is useful in studies of the movement of a specific point or regional source.
MS Determination of Pu Activities and Isotope Ratios
Although counting alpha or beta decay events represents the classical approach that has been used successfully for environmental monitoring studies, determinations of Pu activities and isotopic compositions by MS nonetheless are very attractive. MS is inherently advantageous for determination of long-lived radionuclides; the contrast between MS and decay-counting approaches is detailed elsewhere (4). While determination of 238 Pu in environmental samples by MS generally is precluded by small numbers of atoms and interference from 238 U, MS determinations of 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, and 242Pu by isotope dilution are all well known. 242Pu is available readily as a high-purity standard reference material (NIST 4334g), and its use as a spike isotope is commonplace.
Several MS techniques have been used for the determination of environmental Pu: TIMS, accelerator MS (AMS), resonance ionization MS (RIMS), and inductively coupled plasma MS (ICP-MS). Compared with the aforementioned MS techniques, ICP-MS offers reasonable cost, simple introduction of aqueous solutions, and relatively straightforward operation. Original developments in ICP-MS utilized quadrupole mass analyzers; sector field (SF) mass analyzers applications have become more important in the past 10 years or so. The merits of ICP-MS in radionuclide analysis have long been recognized (5). Arguably, because of its widespread availability, ease of use, relatively low capital cost, and high throughput, ICP-MS is the best-suited MS technique for performing large numbers of Pu determinations in environmental samples.
Applications of ICP-MS in Pu analysis have been expanding rapidly; one major reason is the increasing availability of SF-ICP-MS. For Pu analysis, SF-ICP-MS is superior to quadrupole ICP-MS in three major respects. SF-ICP-MS generally exhibits much better atom-counting efficiencies, on the order of 0.05–0.1% for SF-ICP-MS, versus ± 0.01 % for quadrupole ICP-MS. This efficiency improvement enables the analysis of smaller bulk samples containing smaller absolute amounts of Pu. SF-ICP-MS also exhibits a low background signal of <1 cps, as opposed to backgrounds of a few cps typical of quadrupole ICP-MS. Third, with most SF-ICP-MS devices, it is possible to use medium- or high-resolution conditions to check for many interfering polyatomic ions.
Sample Preparation and Analytical Considerations
The determination of Pu by SF-ICP-MS typically involves dissolution or leaching; separation–preconcentration; and MS measurement. The first two steps strongly resemble those used in classical radiochemical analysis. The analysis commences with dry-ashing, spike isotope addition, and acid leaching with HNO3 or HCl. However, acid leaching fails to recover insoluble, "refractory" forms of Pu, which have been identified in fused particles from the Nevada Test Site (6) and from fire-produced PuO2 particles. Kenna (7) described a procedure for total dissolution with HF-containing acid mixtures, followed by determination of Pu activities and isotopic compositions by SF-ICP-MS. Nygren et al. (8) described the use of a lithium borate for determination of refractory Pu in soils and sediments.
For separation and preconcentration, several different column systems have been used; the procedures based upon anion-exchange resins such as Dowex 1-X8 are based upon the classical alpha spectrometric procedures used for the past several decades by radiochemists. Many recent workers use extraction chromatographic resins such as TEVA (9), which consists of a quaternary ammonium ion immobilized on an inert polymer. The Dowex 1-X8 and TEVA separations initially retain Pu from aqueous HNO3 as anionic [PuIV (NO3 )6 ]2- ; U and matrix elements pass unretained through the first column stage. In SF-ICP-MS, it is critical to remove the matrix elements U and Th from the sample; U will produce isobaric 238 U1 H+ , and excessive amounts of Th can produce elevated background resulting from 232 Th+ and 232 Th16 O+ peak tails. Column washes with HNO3 and HCl are used to remove U and Th, respectively. Pu subsequently is removed from the column by reduction to Pu(III) or with a complexing agent such as oxalate. As is commonly the case with ICP-MS work, the sample preparation is far more time-consuming than are the actual MS determination steps. The determination step typically requires only a few minutes counting time. Sample throughput is 3–10 samples/h and, depending upon the instrument and sample introduction system, detection limits range from ~0.1 to 10 fg for each isotope. One major advantage of ICP-MS is the ability to obtain a mass spectrum in approximately 1 min (Figure 2). These spectra quickly confirm the presence of individual isotopes such as 239Pu and 240Pu, and indicate the suitability of the solution for further peak-jump quantitative analysis.
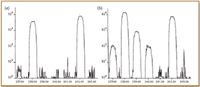
Figure 2. Mass spectral scans of (a) an acid leach blank and (b) a recent sediment sample containing atmospherically deposited Pu. Peaks present in the blank consist of 238U (reagent-derived) and 242Pu (isotope dilution spike, ~50 pg); the recent sediment sample (2 g) exhibits peaks from 237Np, 239Pu, and 240Pu. Note the logarithmic y-scale.
Applications
Several prominent areas of interest have emerged for studies of environmental Pu: 1) evaluating local/regional Pu sources and measuring their significance versus global fallout; 2) understanding the sources, distribution, and geochemistry of Pu in the marine environment; 3) nuclear forensics; and 4) using fallout Pu as a tracer of earth/environmental processes. ICP-MS has been applied to all of these areas; in this article, some brief examples from the author's work will be given for topics 1 and 4.
The 1986 nuclear power plant accident at Chernobyl released an estimated 8.7 × 1013 Bq of 239+240 Pu into the environment (10); although this is much less than global releases of weapons-testing fallout, the Chernobyl plume is regionally very significant. Ketterer et al. (11) used sector ICP-MS in a study of Pu atom ratios in soils from Poland; mixing between global fallout and Chernobyl Pu was found through analysis of archived NdF3 alpha sources. The atom ratios 240Pu/239Pu and 241Pu/239Pu for northeastern Poland samples were both elevated compared with global fallout Pu; a well-defined mixing line was observed (Figure 3). It is believed that northeastern Poland received fallout of nonvolatile debris from the first Chernobyl plume that subsequently was detected in Scandinavia. However, Pu in forest soils and peat bogs of southern Poland was dominated by global fallout Pu.
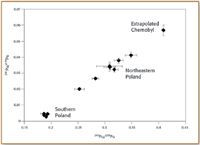
Figure 3. Mixing plot of 241Pu/239Pu versus 240Pu/239Pu for Polish forest soils; error bars are ± one standard deviation.
Dating of recent sediments frequently is determined via atmospherically deposited radionuclides such as 210Pb and 137Cs. The basis of 137Cs dating is that an onset of detection is observed circa 1952, with activity maxima in 1963 (stratospheric fallout) and 1986 (Chernobyl, observed mainly in Europe). The determination of 137Cs is made by gamma spectrometry; although nondestructive, this determination is often time-consuming. An alternative is 239+240Pu; however, the impediment to previous 239+240Pu chronology studies has been the analytical throughput constraints of alpha spectrometry. Because ICP-MS-based 239+240Pu activity measurements can be made rapidly and relatively cheaply, there is considerable potential for the routine use of this method in sediment studies (12).
In addition to providing information about chronology via interpretation of the 239+240Pu activity profile, additional information about the provenance of Pu is possible through 240 Pu/239Pu. One recent study conducted by the author and collaborators determined the sediment chronology in a sediment core from Lake Erie's Eastern Basin (Figure 4). 1.0-g sediment aliquots were prepared by fusion with potassium pyrosulfate (13). The 239+240Pu activity is first detectable at 60 cm depth, reaches a peak at about 45 cm, and then diminishes sharply to the present. Inferred dates are as shown in Figure 4. The 239+240Pu activity profile coincides precisely with the 137 Cs profile. Moreover, the 240Pu/239Pu atom ratios in the five sediment intervals immediately preceding the 1963 239+240Pu activity maximum all are systematically lower than stratospheric fallout ratios (2). The lower 240Pu/239Pu atom ratios most likely result from mixing between stratospheric fallout and tropospheric fallout from the NTS.
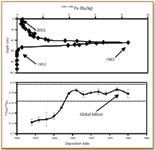
Figure 4. 239+240Pu activity and 240Pu/239Pu atom ratio profiles from a sediment core obtained from Lake Erieôs Eastern Basin; inferred dates are 1952 (Pu first detected), 1963 (maximum Pu activity), and 2002 (sampling date). The global fallout 240Pu/239Pu atom ratio range is from Kelley et al. (2).
Conclusion
Even a brief glimpse of the literature reveals that ICP-MS now has a strong presence in the field of environmental radioactivity and specifically, in its use for measuring activities and isotopic compositions of Pu. In this latter application, the use of SF-ICP-MS is expanding rapidly. The scope of most publications now is shifting from analytical methods development into using SF-ICP-MS data in real-world applications. It is reasonably certain that SF-ICP-MS has sufficient sensitivity to determine Pu activities and isotope ratios in reasonable size samples of fallout-containing material. In this respect, SF-ICP-MS is superior to traditional alpha spectrometric procedures, which are much more time-consuming. It is difficult to imagine that SF-ICP-MS or other MS techniques eventually will replace alpha spectrometry in all laboratories worldwide completely. However, the present trend of interest in SF-ICP-MS is expected to increase. SF-ICP-MS offers advantages of cost, ease of analysis, and access at many laboratories that cannot be equaled by other MS techniques with similar (or better) capabilities for Pu determination; it would be an unexpected development to see many more AMS facilities or TIMS systems used for Pu analysis in upcoming years.
Acknowledgments
Portions of the author's experimental work discussed herein were supported by NSF Grants CHE-0116804 and EAR-0125934. The author also wishes to thank collaborators and students; and J.A.K. and S.M.L. for inspiration toward facing apparent difficulties and challenges in life.
References
1. The data used to produce Figure 1 were obtained from the Department of Homeland Security's Environmental Monitoring Laboratory, Fallout Measurements Database: http://www.eml.doe.gov/databases/fallout/, page accessed 28 June 2005.
2. J.M. Kelley, L.A. Bond, and T.M. Beasley, Sci. Total Environ. 237/238, 483–500 (1999).
3. L.W. Cooper, J.M. Kelley, L.A. Bond, K.A. Orlandini, and J.M. Grebmeier, Marine Chem . 69, 253–276 (2000).
4. J.S. Becker, and H-J. Dietze, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 197, 1–35 (2000).
5. G.P. Russ III, "Isotope ratio measurements using ICP-MS," in Applications of ICP-MS , A.R. Date and A.L. Gray, eds. (Chapman and Hall, New York, 1989), pp. 90–114.
6. T.J. Tamura, J. Environ. Qual. 4, 350–354 (1975).
7. T.C. Kenna, J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 17, 1471–1479 (2002).
8. U. Nygren, I. Rodushkin, C. Nilsson, and D.C. Baxter, J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 18, 1426–1434 (2003).
9. E.P. Horwitz, M.L. Deitz, R. Chiarizia, H. Diamond, S.L. Maxwell III, and M.R. Nelson, Anal. Chim. Acta 310, 63–78 (1995).
10. Y. Muramatsu, W. Rühm. Yoshida, K. Tagami, S. Uchida, and E. Wirth, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 2913–2917 (2000).
11. M.E. Ketterer, K.M. Hafer, and J.W. Mietelski, J. Environ. Radioact. 73, 183–201 (2004).
12. M.E. Ketterer, K.M. Hafer, V.J. Jones, and P.G. Appleby, Sci. Total Environ. 322, 221–229 (2004).
13. S.F. Boulyga, M. Zoriy, M.E. Keterer, and J.S. Becker, J. Environ. Monit. 5, 661–666 (2003).

Trending on Spectroscopy: The Top Content of 2024
December 30th 2024In 2024, we launched multiple content series, covered major conferences, presented two awards, and continued our monthly Analytically Speaking episodes. Below, you'll find a selection of the most popular content from Spectroscopy over the past year.