Validation of Horizon Technology Disk Extraction Technology for US EPA Wastewater Method 625.1
Special Issues
This application note will present the data collected as part of the demonstration of disk solid phase extraction validation for US EPA method 625.1.
Zoe Grosser*, Alicia Cannon*, Michael Ebitson*, Melissa Lever*, Nic Rasnake†, Jessica Bowker†, Allen Fuller†, Chris Johnson†, *Horizon Technology, and †ESC Lab Sciences
The US EPA monitors a variety of chemicals in water that may cause harm to humans or wildlife to minimize exposure. Method 625 was developed by the Office of Science and Technology in the Clean Water program to allow the monitoring of a large suite of semivolatile chemicals in wastewater for compliance with the National Pollution Discharge Elimination System (NPDES). NPDES is a system of permitting that defines the characteristics of water that is released into a waterway, defined by industrial category. The permitting levels are set depending on the waterway’s use. If the waterway is used for recreation or is an important wildlife habitat, the limit may be set lower.
The original method was developed in the early 1980s and has been updated several times since then to allow the use of more modern technology. The latest update has taken place over the last few years and was proposed in a Method Update Rule (MUR) in 2015 which was just published in the Federal Register August 28, 2017 and became effective September 27, 2017 (1). The latest version of the method includes a larger suite of analytes (up to 364) and an extensive set of labeled surrogates to better monitor the method performance throughout the sample preparation and analysis step.
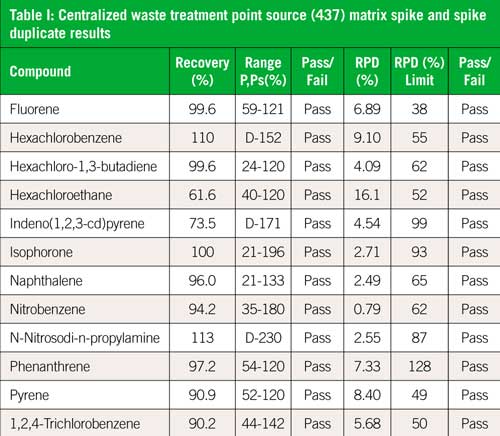
This application note will present the data collected as part of the demonstration of disk solid phase extraction validation for US EPA method 625.1. Nine different wastewater matrices were evaluated and tested against the criteria listed in Table 6 of the method. Sample preparation was performed using the Atlantic® One-pass system, where the water sample is passed through a solid phase extraction (SPE) disk and carbon cartridge once, rather than twice with a pH change between loadings. Automation of the process was achieved using the SPE-DEX® 4790 system (superseded by SPE-DEX 5000). Table I shows the matrix spike and matrix spike duplicate results for a centralized waste treatment point source (437 NPDES category) sample, for selected compounds. The spike recovery and agreement between the duplicates was within criteria for most all analytes. Method detection limits, initial demonstration of compliance, and other wastewater matrices are shown in the full application note (2).
References
- Method 625.1, December 14 revision, can be found in the MUR, February 19, 2015. Or downloaded here: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P100LVHC.PDF?Dockey=P100LVHC.PDF.
- Application Note 117, “Validation of Horizon Technology Disk Extraction Technology for US EPA Wastewater Method 625.1,” available from

Horizon Technology, Inc.
16 Northwestern Drive, Salem, NJ 03079
tel. (603) 893-3663
Website: www.horizontechinc.com

New Study Reveals Insights into Phenol’s Behavior in Ice
April 16th 2025A new study published in Spectrochimica Acta Part A by Dominik Heger and colleagues at Masaryk University reveals that phenol's photophysical properties change significantly when frozen, potentially enabling its breakdown by sunlight in icy environments.