Average Particle Size and Size-Distribution Analysis of BaTiO3 Powder by Ultra-Small-Angle X-ray Scattering
Special Issues
For miniaturization of devices, nanoscale BT research has been actively conducted, along with research on the enhanced dielectric properties of nano-capacitor materials.
BaTiO3 (BT) is a typical ferroelectric material used in capacitors. For miniaturization of devices, nanoscale BT research has been actively conducted, along with research on the enhanced dielectric properties of nano-capacitor materials. The ferroelectricity of BT at room temperature is strongly related to its tetragonal crystal structure. It has been reported that the dielectric constant increases as BT particle size decreases.
However, below a certain critical size, ferroelectricity of BT disappears and it exhibits characteristics of a cubic crystal structure at room temperature. Various measurement methods have been deployed to study the relationship between particle size and structure and the compound's ferroelectricity. Among them, small angle or ultra-small angle X-ray scattering has been used to investigate the particle size of powder materials non-destructively, without dilution. Here, the average particle size and the size distribution of a BT powder are evaluated by ultra-small angle X-ray scattering.
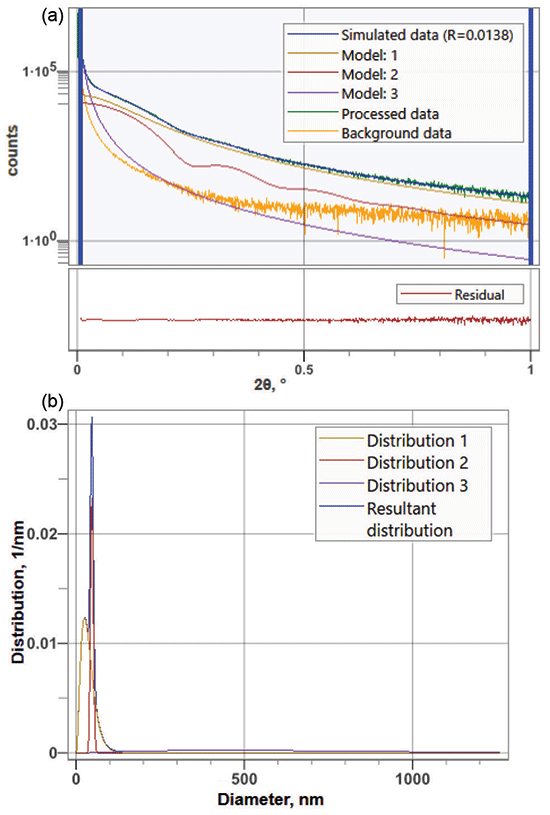
Figure 1: (a) Ultra-small angle X-ray scattering profile of BaTiO3 powder (green line) and the result simulated by three spherical models (blue line), (b) their particle size distributions.
An ultra-small angle X-ray scattering (USAXS) measurement was performed on a commercial BaTiO3 (BT) powder sample having particle diameters of 100 nm or less. The sample was sandwiched between Mylar films with a thickness of 2.5 μm and was measured for about 10 min. Figure 1a shows the USAXS profile and the result calculated by three spherical models. Figure 1b is the particle size distribution obtained from the calculation. As a result, it was found that the primary particle size had an average particle diameter of about 30~50 nm (model 1 and 2), and an aggregated secondary particle diameter of about 700 nm (model 3) (Table I). In addition, BT particles with a diameter of 47 nm are distributed as monodisperse particles (Model 2). USAXS measurements conducted in a short time allow particles from several tens to several hundred nanometers in diameter to be precisely evaluated at the same time. Furthermore, in addition to the particle size distribution, the dispersion state can be analyzed and discussed based on simulated results using the observed data.
Recommended equipment and software
- Automated Multipurpose X-ray Diffractometer SmartLab
- Integrated X-ray Analysis Software SmartLab Studio II (MRSAXS plugin)

Rigaku Corporation
9009 New Trails Drive, The Woodlands, TX 77381
tel. (281) 362-2300, fax (281) 364-3628
Website: www.rigaku.com

LIBS Illuminates the Hidden Health Risks of Indoor Welding and Soldering
April 23rd 2025A new dual-spectroscopy approach reveals real-time pollution threats in indoor workspaces. Chinese researchers have pioneered the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and aerosol mass spectrometry to uncover and monitor harmful heavy metal and dust emissions from soldering and welding in real-time. These complementary tools offer a fast, accurate means to evaluate air quality threats in industrial and indoor environments—where people spend most of their time.
NIR Spectroscopy Explored as Sustainable Approach to Detecting Bovine Mastitis
April 23rd 2025A new study published in Applied Food Research demonstrates that near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) can effectively detect subclinical bovine mastitis in milk, offering a fast, non-invasive method to guide targeted antibiotic treatment and support sustainable dairy practices.
Smarter Sensors, Cleaner Earth Using AI and IoT for Pollution Monitoring
April 22nd 2025A global research team has detailed how smart sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are transforming the detection and management of environmental pollutants. Their comprehensive review highlights how spectroscopy and sensor networks are now key tools in real-time pollution tracking.