Advancements in Low Cost Miniature NIR Spectrometers Enable New Applications in Sample Identification and Quality Control
Application Notebook
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is a powerful technique for rapid and non-destructive material analysis. Scientific breakthroughs over the past several decades have made NIR one of the most powerful tools for research, especially in industries such as food and drug, chemical, oil and gas, and plastics. This technique has mainly been limited to non-portable applications due to instrument size, fragility, and cost. Additionally, Database Search Software or Multivariate Prediction Software must also be employed to extract results; however, user-friendly and cost effective solutions have not been widely available.
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is a powerful technique for rapid and non-destructive material analysis. Scientific breakthroughs over the past several decades have made NIR one of the most powerful tools for research, especially in industries such as food and drug, chemical, oil and gas, and plastics. This technique has mainly been limited to non-portable applications due to instrument size, fragility, and cost. Additionally, Database Search Software or Multivariate Prediction Software must also be employed to extract results; however, user-friendly and cost effective solutions have not been widely available.
Recent advancements in instrument design, size, ruggedness, and cost-reduction, in addition to integration of robust software, have led to new applications and implementations of NIR. Here we present the miniature RED-Wave-NIRX-SR low noise extended wavelength range NIR spectrometer easily predicting different plastic types (Figure 1).

Figure 1: RED-Wave-NIRX-SR low noise extended wavelength range NIR spectrometer (900â2300 nm).
Experimental
The instrumentation used in this demonstration was a miniature RED-Wave-NIRX-SR low noise, extended wavelength range, NIR spectrometer with an integrated 512 element InGaAs linear photodiode array covering the 900–2300 nm wavelength range. The spectrometer has a 25 µm slit to provide optical resolutions of less than 13 nm. The unit was fiber optically coupled to a transmission fixture and a Tungsten halogen illumination source. Several samples each of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS) were acquired from commonly used items found around the laboratory (e.g. containers, bottles, bags, etc.). In each case one sample was used as the plastic type standard and the remaining samples were used as unknown samples. Transmission spectra of the plastic standards were collected and saved into the SpectraWiz Spectral ID Library. Next, the plastic unknown samples were measured and analyzed using the Spectral ID Library Search which uses covariance mathematics to assign a correlation value to each library spectrum.
Results and Conclusion
All unknown plastic samples were correctly matched and identified by the Spectral ID Library Search algorithm and displayed correlation values of greater than 90% for each standard plastic type. Figure 2 shows a correlation value of 91% for the polystyrene samples and displays polystyrenes distinct NIR absorption peaks at 1143, 1680, and 2167 nm from styrenes aromatic C-H combination bands. Likewise, combination bands of Polypropylene's methylenic stretches are visible and quickly used to assign the correct sample match with a correlation value of 96%. The results of this simple experiment show clearly that NIR spectroscopy can be used to identify common plastics and improve sorting of different recycled plastic materials.
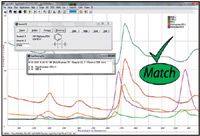
Figure 2: SpectraWiz software displaying raw NIR absorbance spectra (900â2300 nm) of common plastics. The Spectral ID application panel correctly identifies a "Spectral Match" for polystyrene.
The use of multivariate chemometrics further enables a variety of applications such as quantification of copolymers ratios, moisture detection, additive monitoring, and even properties such as melt flow index and molecular weight. Additionally, Database Search Software such as SpectraWiz Spectral ID has been used in portable UV-vis and Raman spectroscopy allowing simple and fast match type analysis for a variety of new applications such as raw material & chemical ID, forensics & counterfeit analysis, food safety, and pharmaceuticals. Low cost, rugged, and miniature instruments like the RED-Wave-NIRX-SR spectrometer are revolutionizing portable and at-line product analysis and enabling quality control never before attainable.
StellarNet, Inc.
14390 Carlson Circle, Tampa, FL 33626
tel. (813) 855-8687, fax (813) 855-8687
Website: www.StellarNet.us

Thermo Fisher Scientists Highlight the Latest Advances in Process Monitoring with Raman Spectroscopy
April 1st 2025In this exclusive Spectroscopy interview, John Richmond and Tom Dearing of Thermo Fisher Scientific discuss the company’s Raman technology and the latest trends for process monitoring across various applications.
A Seamless Trace Elemental Analysis Prescription for Quality Pharmaceuticals
March 31st 2025Quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure compliance with standards like United States Pharmacopoeia <232> and ICH Q3D, as well as FDA regulations. Reliable and user-friendly testing solutions help QA/QC labs deliver precise trace elemental analyses while meeting throughput demands and data security requirements.