
Special Issues
Back by popular demand, Spectroscopy's resident MS expert, Ken Busch, presents a list of common acronyms used in the field.

Special Issues
Back by popular demand, Spectroscopy's resident MS expert, Ken Busch, presents a list of common acronyms used in the field.
Special Issues
The author reviews the Digital Library for the Analytical Sciences (ASDLib) Web site, its philosophy, a summary of its MS resources, and how it can be useful to mass spectrometry practitioners.
Special Issues
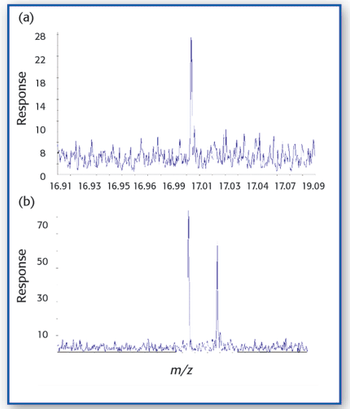
A transportable miniature Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer is used to identify chemical species and remove isobaric interferences in gas analysis. Experimental results use real time direct analysis without the need for additional separation.

Special Issues
The annual event will continue its tradition of promoting knowledge of all things mass spectrometry, with a few new features mixed in.

Special Issues
The European-built Huygens probe made history on January 14 by becoming the first spacecraft to land on Saturn's largest moon. The Huygens gas chromatography–mass spectrometry team concluded that methane rain occurs on the moon, and GC–MS can distinguish between two isotopic forms of carbon — carbon-12 and carbon-13. By comparing the carbon-12/13 ratios it might be possible to pin a biological source to the methane arising from the interior of Titan.
Special Issues
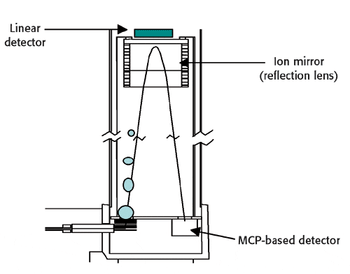
Time-of-Flight (TOF) is rapidly becoming the most popular method of mass separation for proteomics and conventional analytical chemistry. The development of very high temporal resolution ion detectors and low-cost high-speed digitizers has rendered this technique easily deployed and able to produce very high mass resolution. The performance of a TOF mass spectrometer is dependent upon a number of critical components. This article will focus on the ion detector.
Special Issues
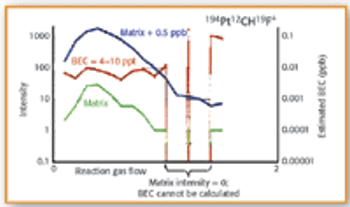
The potential for signal drift, matrix suppression, and spectral interference, in addition to demanding sample preparation, can make geological matrices some of the most difficult to analyze by conventional inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry.
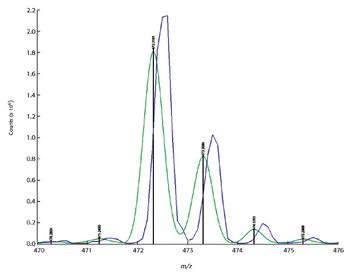
Special Issues
The exploding field of proteomics has highlighted the need to improve the performance of mass spectrometry, both quantitatively and qualitatively. These needs have led instrument manufacturers to produce instruments of increasingly higher quality, but little work has been done to address the fundamental errors inherent in the measurement technique itself. This paper examines these errors and demonstrates that the appropriate mathematical correction of MS data can significantly improve the performance of both low- and high-resolution instruments.

Special Issues
Off-line 2-D LC–MS-MS represents a powerful alternative to on-line methodologies for protein identification from complex proteomes, improving the chromatographic resolution of digest peptide mixtures, even for low-abundance proteins. Here, the authors provide a detailed comparison of the two techniques.