Structure and Thermodynamics of an mAb Biotherapeutic in Different Formulations
The new technique of dynamic multi-mode spectroscopy (DMS) was used to study the stability of a monoclonal antibody biotherapeutic formulated in acetate and lactate buffers. The samples were measured several times over a period of weeks and it became apparent that the antibody behaved differently as it aged in the two formulations, with the lactate formulation imparting greater robustness than the acetate.
The new technique of dynamic multi-mode spectroscopy (DMS) was used to study the stability of a monoclonal antibody biotherapeutic formulated in acetate and lactate buffers. The samples were measured several times over a period of weeks and it became apparent that the antibody behaved differently as it aged in the two formulations, with the lactate formulation imparting greater robustness than the acetate.
Experimental
DMS uses two or more spectroscopic probes to generate full near-or far-UV spectra of a protein as a function of continuously changing temperature, which provides both structural and thermodynamic information in a single, sample-efficient experiment. In this study, each DMS dataset was obtained in under 100 minutes and used only 65 μg of protein. Subsequent analyses of the data were carried out using a proprietary global analysis program, an integral part of the DMS technique.
Results and discussion
Robust Tm values were calculated from the CD temperature profiles by global analysis. Significant differences in the mid-points of the first and third transitions were observed; the mid-points of the second transitions were the same within experimental error. The first transition was lower in the lactate than in the acetate; the third transition was the most significant and best defined in both acetate and lactate buffers and was higher in the lactate formulation by 1.8°C. There was significant variation in the individually calculated enthalpies, an inevitable consequence of the degree of overlap of transitions in these complex systems.
The CD spectra of the DMS data were used to identify changes in the secondary structure of the antibody. Both acetate and lactate formulations maintain the antibody in its mainly β-sheet conformation as they age and, initially, the conformation changes on heating are very similar, with each formulation taking a virtually identical structural pathway to a recognisable unfolded state (Figure 1, top). As the samples age, the denaturation pathway in acetate changes dramatically but remains virtually identical in lactate (Figure 1, bottom), suggesting greater stability.
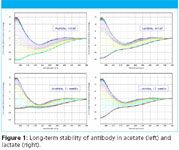
Figure 1
The absorption spectra of the DMS data were used to identify the onset of aggregation. The temperature of onset of aggregation in acetate was found to decrease significantly with sample age whereas no tendency to aggregate was found for the lactate irrespective of the age of the sample.
Conclusions
The results suggest that the antibody is more stable in the lactate than in the acetate formulation despite its significantly lower Tm1, which if taken in isolation might suggest the contrary. It is interesting to note that the data presented here support opinion voiced at a recent biocalorimetry conference (1), that Tm on its own may not be a particularly good indicator of stability and that resistance to aggregation once unfolding has occurred is likely to be a better indicator. The ability of DMS to measure structural, thermodynamic and aggregation behaviour in a single experiment highlights the value of using the technique in formulation testing during biotherapeutic antibody development.
Reference
(1) Applications of Biocalorimetry, Heidelberg, July 7–10 2008.

Applied Photophysics Limited
201–205 Kingston Road • Leatherhead, Surrey, United Kingdom
T +44 1372 386537 • F +44 1372 386477

Enhancing Trace Element Analysis with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
May 15th 2025Elemental analysis is crucial in a wide variety of applications from detecting toxic elements within the environment, to ensuring drinking water is safe for human consumption, to food product safety. ICP-MS—able to measure an atom’s mass—offers low detection limits in the range of parts per trillion (ppt), making it a widely used method that can detect toxic elements well below regulatory limits. This paper expands upon how new ICP-MS technology can meet the challenges associated with heightened demands for element analysis and the hurdles laboratories face when analyzing high-matrix samples.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)








