Polymer Analysis in Accordance with ASTM F2617-08 Using TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards
Application Notebook
This application note demonstrates the analysis of lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium, and bromine in polymers, compliant to ASTM F2617-08. The TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards were used to set up the calibration on Epsilon 5. The accuracy of the calibration is demonstrated by determination of European Reference Material (ERM) EC681k.
Taco van der Maten and PANalytical
This application note demonstrates the analysis of lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium, and bromine in polymers, compliant to ASTM F2617-08. The TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards were used to set up the calibration on Epsilon 5. The accuracy of the calibration is demonstrated by determination of European Reference Material (ERM) EC681k.
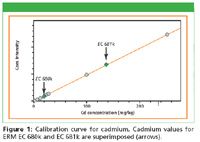
Figure 1
Reference Materials
The TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards were developed and produced by DSM Resolve and PANalytical. A set contains the elements representing the RoHS restricted heavy metals and compounds together with elements representing commonly used additives and fillers. The RoHS Calibration Standards were used to develop F2617-08. ERM EC 681k is produced by the EU Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, Geel, Belgium. The elements present and the concentrations ranges are listed in Table I.
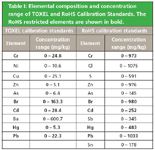
Table I: Elemental composition and concentration range of TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards. The RoHS restricted elements are shown in bold.
Instrumentation
Measurements were performed using a PANalytical Epsilon 5 EDXRF spectrometer, configured with a Sc/W anode X-ray tube. This spectrometer has unique features, including a three-dimensional polarizing optical geometry, 100 kV X-ray tube, up to 15 polarizing and secondary targets and a high resolution Ge detector.
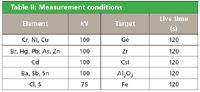
Table II: Measurement conditions
Measurement Procedure
The reference materials were measured using the conditions given in Table II. Optimum count rates were obtained using automatic current (mA) adjustments. The application is set up according to ASTM F2617-08.
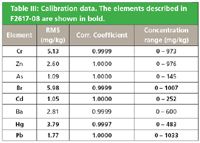
Table III: Calibration data. The elements described in F2617-08 are shown in bold.
Calibration Accuracy
The accuracy of the calibration, using TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards, is presented in Table III. Only the RoHS representing elements and the elements representing commonly used fillers are shown. The calibration RMS value is a statistical comparison (1 sigma) of the certified chemical concentrations and the calculated concentrations in the calibration procedure. The listed RMS and correlation coefficient values illustrate the good calibration accuracy on Epsilon 5. ERM EC 680k and EC 681k reference materials were measured on Epsilon 5 as routine samples. The cadmium intensities are superimposed on the cadmium calibration graph, Figure 1. The cadmium intensities of EC 680k and EC 681k are in excellent agreement with the cadmium regression intensities.
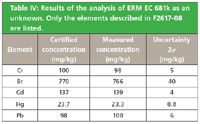
Table IV: Results of the analysis of ERM EC 681k as an unknown. Only the elements described in F2617-08 are listed.
Proven Calibration Accuracy
ERM EC 681k certified reference material was analyzed as an unknown to test the accuracy of the analytical program and to demonstrate compliance to ASTM F2617-08. The data in Table IV demonstrate the excellent agreement between measured and certified concentrations.
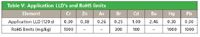
Table V: Application LLD's and RoHS limits
Detection Limits
The detection limits obtained for the elements under study, are an order of magnitude lower than mandated in ASTM F2617-08, Table V. This demonstrates that Epsilon 5 can readily be used for ASTM F2617-08 compliant polymer analysis using TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards. Lower Limits of Detection (LLD) are calculated from:
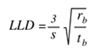
Where:
S = sensitivity (cps/mg/kg)
rb = background count rate (cps)
tb = live time (s)
Conclusion
This application note shows that Epsilon 5 — calibrated with the RoHS Calibration Standards and TOXEL — is fully capable of analyzing lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium, and bromine according to ASTM F2617-08. The agreement between the measured and certified elemental concentration values of ERM EC 681k demonstrates the excellent quality of TOXEL and RoHS Calibration Standards.

PANalytical
117 Flanders Road, Westborough, MA 01581
Tel. (508) 647-1100, (800) 892-7174
Website: www.panalytical.com

Thermo Fisher Scientists Highlight the Latest Advances in Process Monitoring with Raman Spectroscopy
April 1st 2025In this exclusive Spectroscopy interview, John Richmond and Tom Dearing of Thermo Fisher Scientific discuss the company’s Raman technology and the latest trends for process monitoring across various applications.
A Seamless Trace Elemental Analysis Prescription for Quality Pharmaceuticals
March 31st 2025Quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure compliance with standards like United States Pharmacopoeia <232> and ICH Q3D, as well as FDA regulations. Reliable and user-friendly testing solutions help QA/QC labs deliver precise trace elemental analyses while meeting throughput demands and data security requirements.