Measuring the Carrier Lifetime of Perovskites Using Time-Resolved Photoluminescence

Halide perovskite photovoltaic cells have attracted tremendous attention in recent years, due to the rapid rise of their solar cell efficiencies, which have increased from 9% in 2012 to over 25% by 2019, and are now competitive with crystalline silicon (1,2). In this application note, time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy is shown to be a powerful tool for investigating and optimizing the behavior of perovskites through the measurement of charge carrier lifetimes.
Experimental
Methyl ammonium lead iodide (MAPI) perovskite films were deposited on quartz discs, using the methylamine/acetonitrile route (3), followed by annealing at 100 °C. Photoluminescence lifetimes were measured using an Edinburgh Instruments FLS1000 photoluminescence spectrometer equipped with an EPL-405 pulsed diode laser, a PMT-900 detector, and time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) counting electronics.
Results
During the fabrication of perovskite solar cells, the perovskite layer is first deposited by spin-coating, and the layer is then annealed at a high temperature to complete the film formation process. The temperature and duration of this annealing step can have a dramatic impact on the microstructure of the perovskite layer and on the efficiency of the photovoltaic cell.
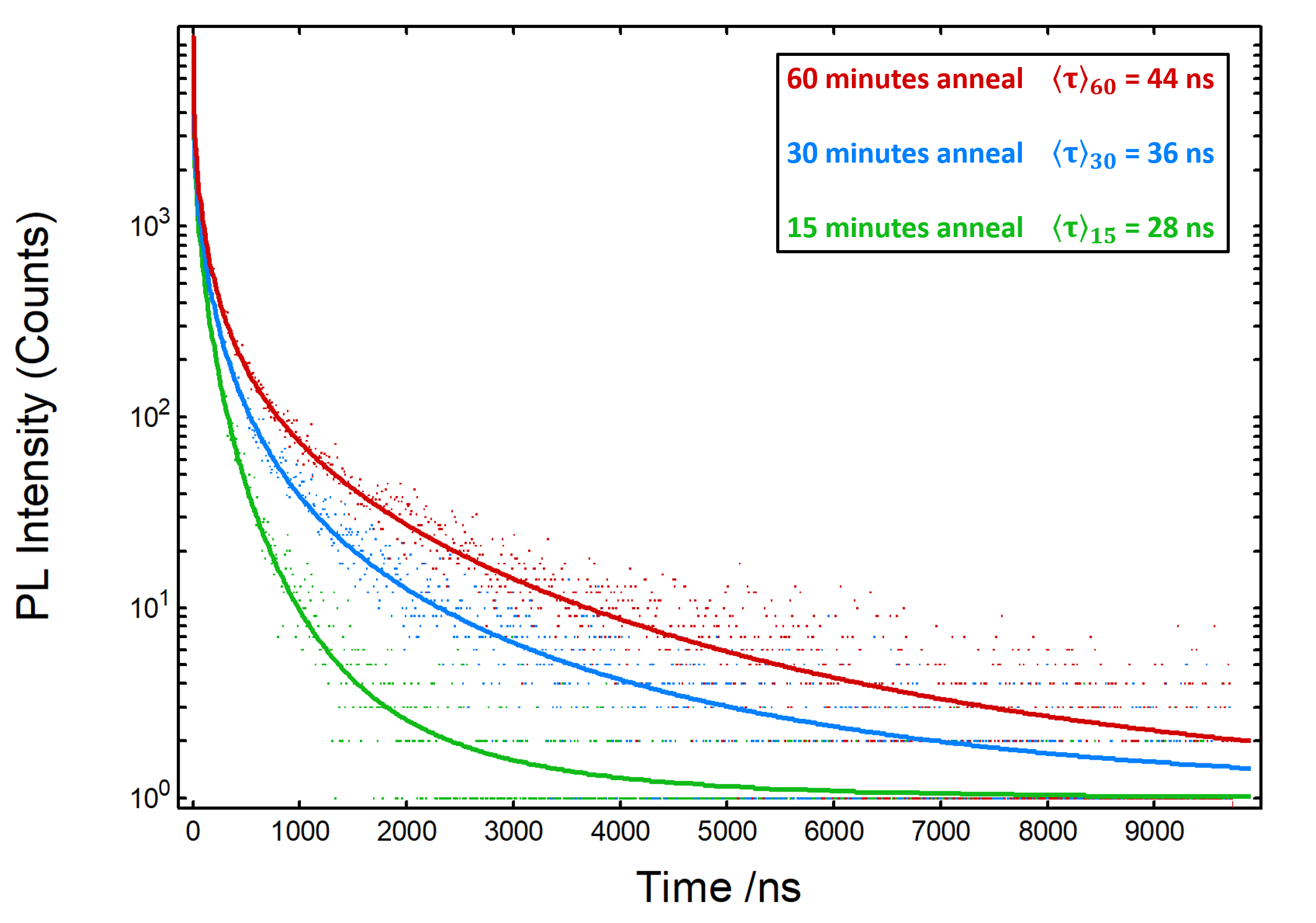
The photoluminescence decays of three MAPI films fabricated with different annealing times were measured using TCSPC and fit with stretched exponential decays using the Fluoracle® software of the FLS1000 (Figure 1). As the annealing time is increased from 15 to 60 min, the mean lifetime of the photoluminescence decay was found to increase from 28 to 44 ns.
Figure 1: Photoluminescence decays of three MAPI perovskite thin films that were annealed for 15, 30, and 60 min. Excitation source = EPL-405 pulsed diode laser, Rep Rate = 100 kHz, λem = 780 nm, Δλem = 10 nm.
Conclusion
The mean lifetime of the MAPI films was measured using TCSPC with the FLS1000 photoluminescence spectrometer and was found to increase with annealing time, indicating that longer annealing extends the average charge carrier lifetime which may improve solar cell efficiency.
References
- NREL Efficiency Chart, Rev. 11-05-2019.
- M. A. Green, Y. Hishikawa, E. D. Dunlop, D. H. Levi, J. Hohl-Ebinger, and A. W. Y. Ho-Baillie, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 26, 3–12 (2018).
- N. K. Noel, S. N. Habisreutinger, B. Wenger, M. T. Klug, M. T. Hörantner, M. B. Johnston, R. J. Nicholas, D. T. Moore and H.J. Snaith, Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 145–152 (2017).
Edinburgh Instruments
2 Bain Square, Kirkton Campus, Livingston, EH54 7DQ, UK
tel. +44 1506 425 300
Website: www.edinst.com

New Study Reveals Insights into Phenol’s Behavior in Ice
April 16th 2025A new study published in Spectrochimica Acta Part A by Dominik Heger and colleagues at Masaryk University reveals that phenol's photophysical properties change significantly when frozen, potentially enabling its breakdown by sunlight in icy environments.
Advanced Raman Spectroscopy Method Boosts Precision in Drug Component Detection
April 7th 2025Researchers in China have developed a rapid, non-destructive Raman spectroscopy method that accurately detects active components in complex drug formulations by combining advanced algorithms to eliminate noise and fluorescence interference.