Trace Elements in Aqueous Solution with UltraCarry®
Application Notebook
The Rigaku NEX CG combines secondary and polarization target excitation, with a high performance SDD detector, to deliver optimal EDXRF sensitivity. In conjunction with UltraCarry, the NEX CG is an ideal tool for the trace elemental analysis of aqueous solutions down to parts-per-billion levels. This technique is suitable for many applications, including: 1) monitor effluents, waste streams, and discharge waters; 2) screen for common metals; 3) measure hazardous elements; 4) QC of production rinse waters; 5) pavement run-off; 6) storm water run-off; 7) agricultural run-off; 8) site remediation; and 9) soil leachates.
Trace element analysis of aqueous-based solutions is important in many areas, such as industrial manufacturing, quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) processes, environmental monitoring and remediation, as well as agriculture and general research. To meet the challenges of trace analysis into the ppb range, Rigaku offers the NEX CG EDXRF analyzer and the UltraCarry sample preparation disk. With the Rigaku system, trace analysis can be carried out by non-technical operators and experts alike, without the need for special scientific training and costly, complicated, time consuming sample preparation.
Elemental analysis of aqueous solutions into the low ppm and sub-ppm concentration ranges was demonstrated, using the advanced Cartesian geometry Rigaku NEX CG Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence (EDXRF) spectrometer in conjunction with the patented UltraCarry® sample preparation technique.
Experiment
UltraCarry is a patented disposable (single-use) sample carrier used to preconcentrate aqueous samples into a uniform thin film that is optimized for the suppression of background noise. This approach dramatically improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the measurement, resulting in up to two orders of magnitude improvement in the lower detection limit (LLD), for both heavy and light elements, relative to conventional bulk liquid sample presentation.
The design is comprised of a ring-shaped support fitted with an X-ray transmissive film and central analytical pad. This design allows the liquid sample to dry in an even single layer, eliminating or minimizing the formation of concentric rings of dry sample material, giving a more consistent and repeatable XRF measurement. Using the automatic sample changer, up to 15 samples can be measured in a single batch without operator intervention.
Figure 1: UltraCarry being loaded.
As shown in Figure 1, 200 µL of each sample was pipetted onto the center of the UltraCarry pad. Samples were then dried using a vacuum oven (75 torr at 68 °C for 15 min), followed by direct analysis with the Rigaku NEX CG. A standardless calibration method was built using the Rigaku RPF-SQX fundamental parameters (FP) template for UltraCarry. RPF-SQX is an advanced FP program that automatically deconvolutes spectral peaks and models the thin film sample matrix using first principles. To demonstrate the standardless FP method, one certified ICP standard, containing common metals, was analyzed for 1200 s. Results are shown in Figure 2.
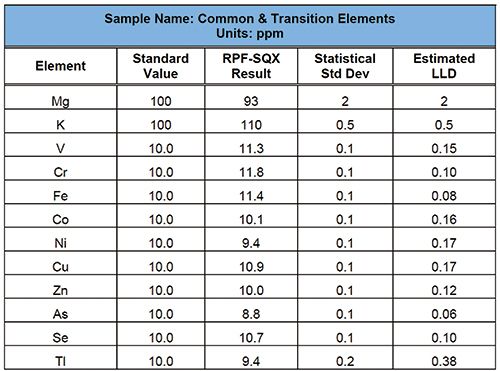
Figure 2: Results of standardless analysis.
Conclusion
The Rigaku NEX CG combines secondary and polarization target excitation, with a high performance SDD detector, to deliver optimal EDXRF sensitivity. In conjunction with UltraCarry, the NEX CG is an ideal tool for the trace elemental analysis of aqueous solutions down to parts-per-billion levels. This technique is suitable for many applications, including: 1) monitor effluents, waste streams, and discharge waters; 2) screen for common metals; 3) measure hazardous elements; 4) QC of production rinse waters; 5) pavement run-off; 6) storm water run-off; 7) agricultural run-off; 8) site remediation; and 9) soil leachates.
References
(1) S. Fess, EDXRF Application Note #1011: Trace Elements in Aqueous Solution with UltraCarry®, Rigaku Press (2010).

Applied Rigaku Technologies, Inc.
9825 Spectrum Drive, Bldg. 4, Suite 475, Austin, TX 78717
tel. +1 (512) 225-1796, fax 1 (512) 225-1797
Website: www.rigakuEDXRF.com, email: info@rigakuEDXRF.com

LIBS Illuminates the Hidden Health Risks of Indoor Welding and Soldering
April 23rd 2025A new dual-spectroscopy approach reveals real-time pollution threats in indoor workspaces. Chinese researchers have pioneered the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and aerosol mass spectrometry to uncover and monitor harmful heavy metal and dust emissions from soldering and welding in real-time. These complementary tools offer a fast, accurate means to evaluate air quality threats in industrial and indoor environments—where people spend most of their time.
Atomic Perspectives: Highlights from Recent Columns
March 3rd 2025“Atomic Perspectives,” provides tutorials and updates on new analytical atomic spectroscopy techniques in a broad range of applications, including environmental analysis, food and beverage analysis, and space exploration, to name a few. Here, we present a compilation of some of the most popular columns.