Advancements in Low Cost Miniature NIR Spectrometers Enable New Applications in Product Analysis and Quality Control
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a powerful technique for rapid and nondestructive material analysis. Scientific breakthroughs over the past several decades have made NIRS one of the most powerful tools for research, especially in industries such as food and drug, chemical, oil and gas, and plastics. This technique has mainly been limited to nonportable applications due to instrument size, fragility, and cost.
Jason Pierce, StellarNet, Inc.
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a powerful technique for rapid and nondestructive material analysis. Scientific breakthroughs over the past several decades have made NIRS one of the most powerful tools for research, especially in industries such as food and drug, chemical, oil and gas, and plastics. This technique has mainly been limited to nonportable applications due to instrument size, fragility, and cost. Additionally, multivariate software for calibration and prediction must also be employed to extract results; however, user-friendly and cost effective solutions have not been widely available.
Recent advancements in instrument design, size, ruggedness, and cost-reduction, in addition to integration of a robust chemometrics software package, have led to new applications and implementations of NIRS. Here we present the miniature DWARF-Star NIR spectrometer (5 in. × 3 in. × 2 in.) easily predicting concentrations of dietary supplements, such as amino acids and natural products.
Experimental
The instrumentation used in this demonstration was an ultra-portable StellarNet DWARF-Star NIR spectrometer with an integrated 512 element InGaAs linear photodiode array covering the 900–1700 nm wavelength range. The unit was fiber optically coupled to a reflectance fixture with an internal Tungsten Halogen lamp. Reflectance spectra of pure components and mixtures of Glutamine, L-Arginine, and Creatine were collected and analyzed using the Eigenvector PLS toolbox®. Predictive calibration models were developed using the partial least square (PLS) regression method with several preprocessing techniques, such as multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), mean centering, and 1st derivative. StellarNet software for both LabVIEW and SpectraWiz allow for simple integration of the Eigenvector Solo Predictor to allow real-time statistical analysis and final result.
Results and Conclusion
Predictive calibration models for the three components were easily and quickly developed. R2 values greater than 0.94 and RMSEC values less than 6 weight percent were attained. Raw spectra, as well as a plot of the cross-validated predicted value vs. the actual value of L-Arginine are shown in Figure 1. Every application has acceptable values of uncertainty and error, therefore calibration models and experimental procedure must be optimized to meet specific requirements.
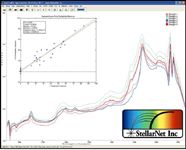
Figure 1: SpectraWiz software interface displaying raw NIR reflectance spectra of dietary supplement powders with inset multivariate calibration model.
Low cost, rugged, and miniature instruments like the DWARF-Star NIR spectrometer are revolutionizing NIRS, enabling new applications and implementation, such as portable and at-line product analysis and quality control never before attainable. In this demonstration quantitative analysis of multi-component mixtures of amino-acids and products would prove beneficial for supplement producers, suppliers, and distributors and would provide a means for low cost analysis and quality control.
Miniature NIR spectrometers offer flexible solutions for a broad range of new applications requiring portability and a small footprint. In the field, the monitoring of fresh produce for moisture and soluble solids will provide more information on ripening stages. And in the meat processing industry contaminants and disease can be reduced by utilizing NIR systems to inspect equipment. Likewise, the fuel and ethanol industry will be revolutionized by improving analysis methods for incoming grains for moisture, starch, and proteins. As scientific advancements over the past several decades have made NIRS one of the most powerful tools for scientific research, the advent of low cost, rugged, and portable NIR devices will provide solutions for a multitude of new applications.
StellarNet, Inc.
14390 Carlson Circle, Tampa, FL 33626
tel. (813) 855-8687, fax (813) 855-8687
Email: ContactUs@StellarNet.us, Website: www.StellarNet.us

AI Shakes Up Spectroscopy as New Tools Reveal the Secret Life of Molecules
April 14th 2025A leading-edge review led by researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and MIT explores how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the study of molecular vibrations and phonon dynamics. From infrared and Raman spectroscopy to neutron and X-ray scattering, AI is transforming how scientists interpret vibrational spectra and predict material behaviors.
Real-Time Battery Health Tracking Using Fiber-Optic Sensors
April 9th 2025A new study by researchers from Palo Alto Research Center (PARC, a Xerox Company) and LG Chem Power presents a novel method for real-time battery monitoring using embedded fiber-optic sensors. This approach enhances state-of-charge (SOC) and state-of-health (SOH) estimations, potentially improving the efficiency and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles (xEVs).
New Study Provides Insights into Chiral Smectic Phases
March 31st 2025Researchers from the Institute of Nuclear Physics Polish Academy of Sciences have unveiled new insights into the molecular arrangement of the 7HH6 compound’s smectic phases using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy.