Dangerous Toys: Rigid Testing Routines Required to Assure Our Children's Safety
Toys conjure up the images of happy little children playing safely with their dolls and model cars but lately, those images have become tarnished by some well publicized recalls of toys made in China. With Chinese made toys accounting for well over 80% of the American market, and dolls even higher, it is understandable that there is general loss of confidence in the toy industry.
The European Union (EU) has a directive RoHS (restriction of hazardous substances) that places strict limits on the amount of heavy metals such as lead, cadmium and mercury that are allowed in consumer goods. Since it applies to all products entering Europe, it should affect all countries that export toys. In theory, this should protect consumers throughout the world but manufacturers do cut corners and it is impossible for the individual countries to verify that every batch of every toy that enters that market is in compliance. Therefore, it is in the best interests of everyone, including the manufacturers, to prove through a vigorous internal quality control program, that their products are safe.
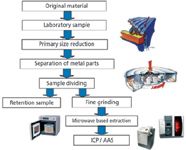
Sample preparation steps
In order to accurately detect trace amounts of such heavy metals, any testing method must produce reliable, reproducible results and be relatively simple and quick to perform. The method must also be able to detect trace amounts hidden inside the item as well as on the surface since this is the only certain way of knowing whether or not the item is safe for the consumer.

Figure 1: Cutting Mill SM 2000 for initial size reduction of a plastic doll pieces to 3â4 mm.
In order for testing to be carried out, the toy or item has to be turned into a sample that can be presented to the analyzer that will be used This requires size reduction and homogenization to ensure that the final sample represents as closely as possible the exact composition of the original item including any accessory parts.
Primary Size Reduction
Initially, the toy should be dismantled into its various components and separated into different analysis groups (e.g. plastics of different colors, electronic parts, rubber etc.). In the next step, these items should be processed in a mill such as the Heavy Duty Cutting mill SM 2000 to produce a size of 3–4 mm. This mill, with its offset hard-metal cutting bars, is ideally suited for this preliminary size reduction of such heterogeneous materials.
Sampling, Dividing, and Fine Grinding
In order to maintain the representative nature or the material, this ground sample should be divided into representative sub-samples using a spinning riffler such as the Retsch PT 100 or PK 1000. The sub-sample(s) produced in this step are further homogenized in the Ultra-Centrifugal Mill ZM 200 which achieves a final size below 200 μm in a very short time and in addition, is very gentle on the material. It is recommended that liquid nitrogen or dry ice be used to improve the breaking properties of the material during this step; at the same time this will help preserve any volatile substances which might otherwise be affected by the frictional heat generated during grinding. Heavy-metal-free grinding tools are available for both mills so that subsequent analyses are not influenced by trace amounts of material from the grinding tools.
Depending on the type of toy, it may also be necessary to analyze fibrous materials such as clothing or hair. These materials can be best processed in the Mixer Mill Mill MM 301 or MM 400 which homogenizes sample volumes up to 40 mL in only 1–2 min. The screw-capped grinding jars, complete with sample and grinding balls, are cooled in liquid nitrogen before being clamped in the mill. This external cooling eliminates the need for any additional cooling during grinding and ensures that the whole process is carried out efficiently and quickly.
Analysis
The complete procedure of preparing a heterogeneous toy sample for subsequent analysis as described above takes about 30 minutes including additional preparation steps such as pelletizing. After that, hazardous substances can be detected by analyzing the dry sample with X-ray fluorescence (heavy metals) or NIR (plasticizers) or, after wet extraction, with AAS or ICP-MS (heavy metals).
All laboratory mills mentioned in this article can be equipped with grinding tools for heavy-metal-free sample preparation. This ensures that the results of the subsequent analyses are not influenced by undesired sample contamination from trace elements in the grinding tools.

Retsch, Inc.
74 Walker Lane, Newtown, PA 18940
Tel. (866) 473-8724

Thermo Fisher Scientists Highlight the Latest Advances in Process Monitoring with Raman Spectroscopy
April 1st 2025In this exclusive Spectroscopy interview, John Richmond and Tom Dearing of Thermo Fisher Scientific discuss the company’s Raman technology and the latest trends for process monitoring across various applications.
A Seamless Trace Elemental Analysis Prescription for Quality Pharmaceuticals
March 31st 2025Quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure compliance with standards like United States Pharmacopoeia <232> and ICH Q3D, as well as FDA regulations. Reliable and user-friendly testing solutions help QA/QC labs deliver precise trace elemental analyses while meeting throughput demands and data security requirements.